您的位置:首页 > 产品中心 > Anti-Huntingtin
Anti-Huntingtin
| 产品编号: | 4109031 |
| 规格: | from rabbit, purified by affinity chromatography |
| 包装规格: | 25 μG,100 μG |
| 产品类别: | 进口试剂 |
| 品牌: | Sigma-Aldrich |
| 优惠价: | 立即咨询 |
产品别名
Anti-Huntingtin
Huntington disease protein, HD protein
基本信息
| eCl@ss | 32160702 |
| NACRES | NA.41 |
| General description【一般描述】 | Huntingtin (UniProt: P42858; also known as Huntington disease protein, HD protein) is encoded by the HTT (also known as HD, IT15) gene (Gene ID: 3064) in human. The protein is found in the perinuclear region along with microtubules, and in the centrosomal region along with gamma-tubulin. It is expressed in the brain and is mainly found in the cerebellar cortex, the neocortex, the striatum, and the hippocampal formation. Huntingtin is necessary for neuronal survival and is involved in synaptic vesicle trafficking, microtubule binding and may also have a role in apoptosis. It plays a role in microtubule-mediated transport and vesicle function. Huntingtin protein contains a nuclear export signal (aa 2395-2404) and 5 HEAT (Huntington, Elongation Factor 3, PR65/A, TOR) domains. Huntingtin protein is cleaved by apopain downstream of the polyglutamine stretch and the resulting N-terminal fragment is cytotoxic and provokes apoptosis. Phosphorylation at Serine 1179 and 1199 by CDK5 in response to DNA damage in nuclei of neurons protects neurons against polyglutamine expansion as well as DNA damage mediated toxicity. Mutations in HTT gene cause Huntington disease that is characterized by involuntary movements (chorea), general motor impairment, psychiatric disorders and dementia. Wild-type huntingtin and anti-huntingtin antibody reduces aggregation and cellular toxicity of the mutant huntingtin form in mammalian cell models of Huntington disease. |
| Specificity【特异性】 | This rabbit polyclonal antibody detects Huntington disease protein in human and mouse brain. It targets an epitope within 180 amino acids from the N-terminal region. |
| Immunogen【免疫原】 | GST/His-tagged recombinant fragment corresponding to 180 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human Huntington disease protein . Epitope: N-terminus |
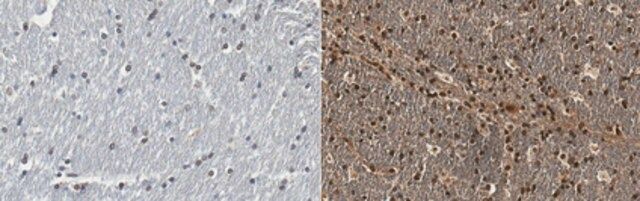
| Application【应用】 | Anti-Huntingtin, Cat. No. ABN903, is a highly specific rabbit polyclonal antibody that targets Huntington Disease Protein and has been tested for use in Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) and Western Blotting. Western Blotting Analysis: 2 µg/mL from a representative lot detected Huntingtin in mouse brain tissue lysate. Research Category Neuroscience |
| Quality【质量】 | Evaluated by Immunohistochemistry in human cerebral cortex and human huntington′s diseased brain tissues. Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A 1:50-250 dilution of this antibody detected Huntingtin in human cerebral cortex and human Huntington′s diseased brain tissues. |
| Physical form【外形】 | Purified rabbit polyclonal antibody in buffer containing 0.1 M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl with 0.05% sodium azide. Affinity Purified |
| Other Notes【其他说明】 | Concentration: Please refer to lot specific datasheet. |
产品性质
| biological source【生物来源】 | rabbit |
| Quality Level【质量水平】 | 100 |
| antibody form【抗体形式】 | affinity isolated antibody |
| antibody product type | primary antibodies |
| clone【克隆】 | polyclonal |
| purified by【纯化方式】 | affinity chromatography |
| species reactivity | mouse, human |
| packaging【包装】 | antibody small pack of 25 μg |
| technique(s) | immunohistochemistry: suitable (paraffin) western blot: suitable |
| UniProt accession no.【UniProt登记号】 | P42858 |
| shipped in【运输】 | ambient |
| Gene Information | human ... HTT(3064) |
产品说明
| Target description【目标描述】 | 347.60 kDa calculated. |
| Storage and Stability【储存及稳定性】 | Stable for 1 year at 2-8°C from date of receipt. |
| Disclaimer【免责声明】 | Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals. |





