您的位置:首页 > 产品中心 > Proteasome Inhibitor Set I-Calbiochem
Proteasome Inhibitor Set I-Calbiochem
| 产品编号: | 4061739 |
| 规格: | The Proteasome Inhibitor Set I controls the biological activity of Proteasome. This small molecule/inhibitor is primarily used for Protease Inhibitors applications. |
| 包装规格: | 1 SET |
| 产品类别: | 进口试剂 |
| 品牌: | Sigma-Aldrich |
| 优惠价: | 立即咨询 |
产品性质
| Quality Level【质量水平】 | 100 |
| form【形式】 | solid |
| manufacturer/tradename | Calbiochem® |
| storage condition【储存条件】 | OK to freeze |
| shipped in【运输】 | ambient |
| storage temp.【储存温度】 | −20℃ |
| packaging【包装】 | 1 set in Glass bottle |
基本信息
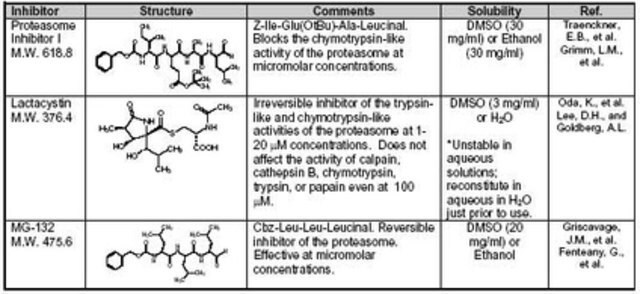
| General description【一般描述】 | Proteasomes are large multi-subunit protease complexes, localized in the nucleus and cytosol, which selectively degrade intracellular proteins. They play a major role in the degradation of many proteins involved in cell cycling, proliferation, and apoptosis. A vast majority of short-lived proteins are degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. A protein marked for degradation is covalently attached to multiple molecules of ubiquitin (Ubq), a highly conserved 76-amino acid (8.6 kDa) protein, which escorts it for rapid hydrolysis to the multi-component enzymatic complex known as the 26S proteasome. The proteolytic core of this complex, the 20S proteasome, contains multiple peptidase activities and functions as the catalytic machine. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway plays a major role in the breakdown of abnormal proteins that result from oxidative stress and mutations that might otherwise disrupt normal cellular homeostasis. The reactive oxygen species can promote partial unfolding of the proteins, exposing its hydrophobic domains to proteolytic enzymes of the 20S complex. Rapid degradation of defective enzymes, as seen in diseases caused by metabolic abnormalities, also occurs in the proteasome. The Ubq-proteasome pathway has also been implicated in several forms of malignancy, in the pathogenesis of several genetic diseases, and in the pathology of muscle wasting. It is also involved in the destruction of proteins that participate in cell cycle progression, transcription control, signal transduction, and metabolic regulation. |
| Biochem/physiol Actions【生化/生理作用】 | Primary Target MPC Secondary Target NF-κB activity |
| Warning【警告】 | Toxicity: Standard Handling (A) |
| Other Notes【其他说明】 | Grimm, L.M., et al. 1996. EMBO J.15, 3835. Griscavage, J.M., et al. 1996. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA93, 3308. Lee, D.H., and Goldberg, A.L. 1996. J. Biol. Chem.271, 27280. Oda, K., et al. 1996. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.219, 800. Fenteany, G., et al. 1995. Science268, 726. Traenckner, E.B., et al. 1994. EMBO J.13, 5433. |
| Legal Information【法律信息】 | CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany |




